Wind Energy: A Deep Dive into Canada's Renewable Energy Future

Wind Energy in Canada
The urgency of addressing climate change demands a rapid transition to clean and sustainable energy sources. Amongst them, wind energy emerges as a powerful and readily available resource, harnessing the kinetic energy of moving air to generate electricity without harmful emissions. This potential has not gone unnoticed in Canada, where wind is poised to play a transformative role in creating a more sustainable future. This report aims to provide a detailed examination of wind energy, focusing on its technical aspects, environmental implications, and market developments, with a particular emphasis on its unique place within Canada's renewable energy landscape.
How Wind Turbines Work
The electricity generation process begins with the kinetic energy of the wind turning the rotor blades. Key components, such as the rotor, generator, nacelle, and tower, work in tandem to convert this kinetic energy into electrical power and this is how wind’s energy is converted into electrical power.
Types of Wind Turbines
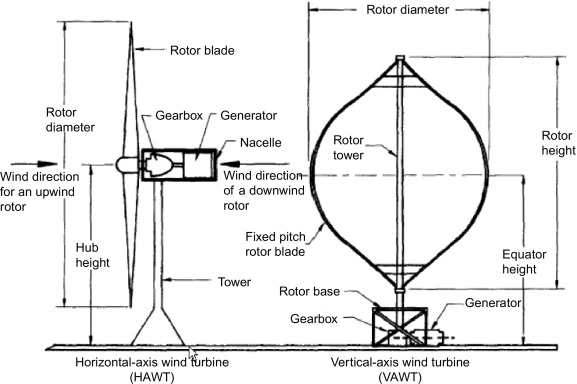
Horizontal-axis wind turbines (HAWTs) are some of the most widely used wind turbines, their large blades resembling propellers as they rotate around a horizontal axis. However, vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWTs) offer unique advantages in urban environments and low-wind areas due to their vertical blade orientation. Regardless of their design, the fundamental principle remains the same: wind turning the blades creates lift and torque, driving a shaft connected to a generator, transforming wind's kinetic energy into electricity.
Site Considerations and Environmental Impact
The optimal location for a wind farm requires a delicate balancing act between wind availability, grid proximity, and environmental responsibility. Strong and consistent winds are essential for maximizing energy generation, while proximity to existing transmission lines minimizes energy losses during transmission. However, wind farms can also raise environmental concerns, including potential impacts on bird and bat populations, noise pollution, and visual alterations to landscapes. Careful planning, rigorous environmental assessments, and mitigation strategies are crucial to minimizing these concerns and ensuring responsible development.
Innovative Technologies and Approaches in Wind Power Generation
The wind energy sector is a dynamic landscape, constantly evolving and propelled by innovative technologies. The following are some of the innovative technologies being used in the wind industry:
Cutting-Edge Blade Designs:
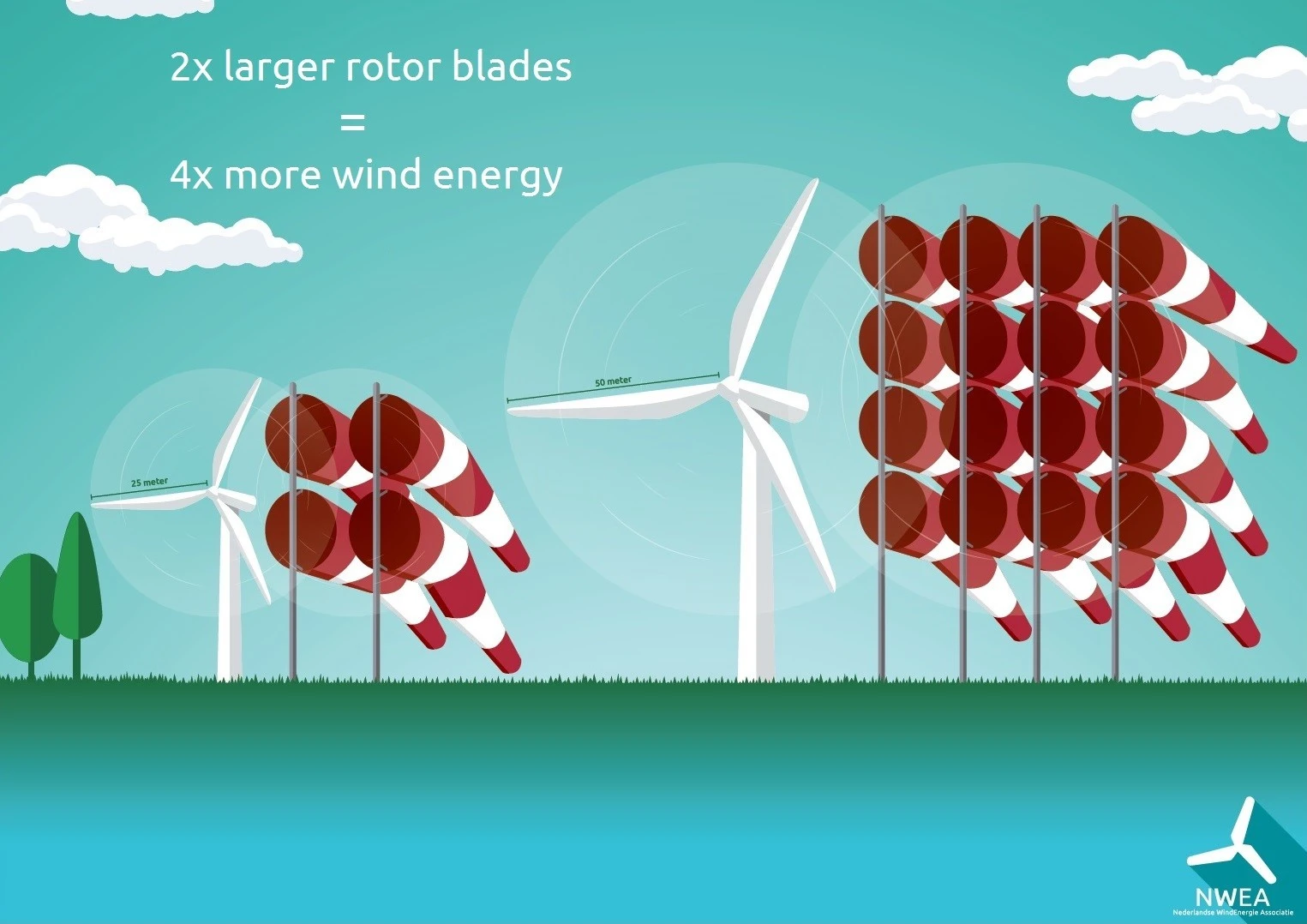
- Larger Blades, Greater Efficiency: Modern wind turbines feature colossal blades exceeding 100 meters in length, capturing significantly more wind energy compared to their predecessors. Advancements in materials like carbon fiber enable these colossal structures while maintaining lightweight properties.
- Smart Blades with Adaptive Pitch: The next generation of blades incorporates built-in sensors and advanced control systems, allowing them to dynamically adjust their pitch angle based on real-time wind conditions. This optimization maximizes energy capture across diverse wind speeds, enhancing overall efficiency.
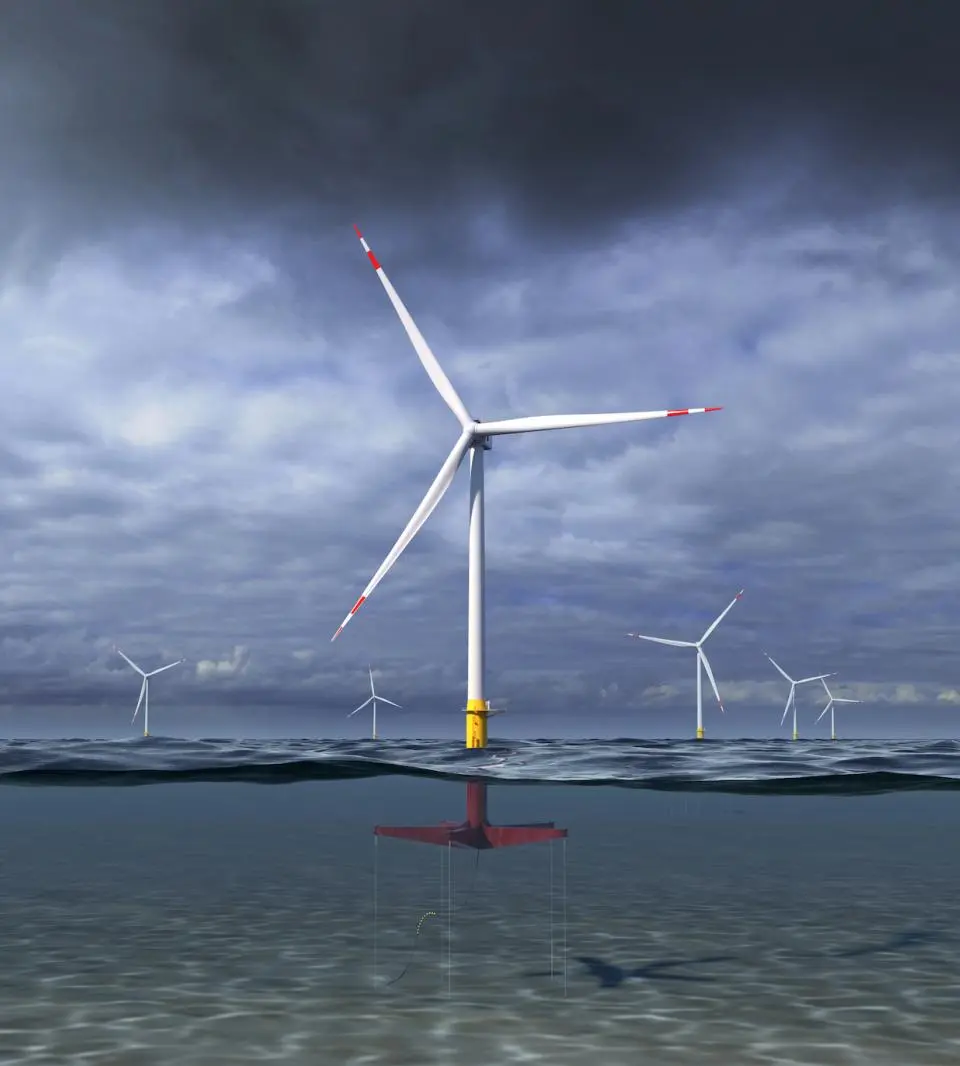
Offshore Wind Farms:
- Floating Turbines for Deeper Waters: Traditional fixed-bottom wind farms face limitations in deeper waters. Floating turbines, anchored to the seabed but buoyant on the surface, offer a solution. These innovative designs are being tested and deployed, unlocking vast offshore wind potential.
- Interconnected Arrays for Power Transmission: Multiple offshore turbines are interconnected in wind farms, transmitting generated electricity via underwater cables to onshore substations. High-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission technology minimizes energy losses over long distances, maximizing the efficiency of offshore wind power delivery.
- Multi-Use Platforms for Sustainability: Offshore wind farms can be combined with other marine activities like aquaculture or desalination plants, creating multi-use platforms that optimize ocean space utilization and promote sustainable development.

Use of Wind Power in the World Energy Mix
Globally, wind energy is experiencing a remarkable surge. In 2022, it accounted for 10.3% of global electricity generation, with China and the United States leading the way.
Although Canada started later, it is rapidly catching up, with wind now constituting the second-largest source of renewable energy, contributing 6.1% of its electricity production in 2022 (NEWS RELEASE: New 2023 Data Shows 11.2% Growth for Wind, Solar & Energy Storage – Canadian Renewable Energy Association, n.d.). Canada has set ambitious targets, aiming to increase this share to 20% by 2025, showcasing its commitment to a clean and sustainable energy future (Wind Vision 2025: Powering Canada’s Future | Climate Technology Centre & Network | Fri, 09/08/2017, n.d.). With its vast wind resources and ambitious targets, Canada stands at a pivotal moment in its energy transition. However, several challenges remain. Grid infrastructure needs modernization to accommodate increasing wind power penetration, which requires significant investment and collaboration between federal, provincial, and territorial governments. Additionally, community engagement and transparent communication are crucial for addressing concerns and building local support for wind farm development.
Conclusion
Wind energy presents a compelling solution in the fight against climate change. Its abundance, minimal emissions, and technological advancements make it a crucial player in the transition to a sustainable future. While environmental considerations, grid integration challenges, and community concerns remain, ongoing innovation, responsible development, and robust policy frameworks offer promising solutions. As Canada embarks on its ambitious wind energy targets, one question lingers: can wind truly become the backbone of a clean and sustainable energy future for the nation and the world? The answer likely lies in our collective commitment to addressing these challenges and harnessing the full potential of this powerful renewable resource.
