Transformer Oil Filtration: Process, Analysis and it's Importance
Is your transformer old and the recent oil test gave a very low and dangerous BDV value? Then it’s time for your transformer to undergo oil filtration process. In these article we will explore the importance of transformer oil filtration process in a preventive maintenance program and the complete process of filtering oil in order to increase its insulation property and life.
Why Transformer Oil Filtration is Required?
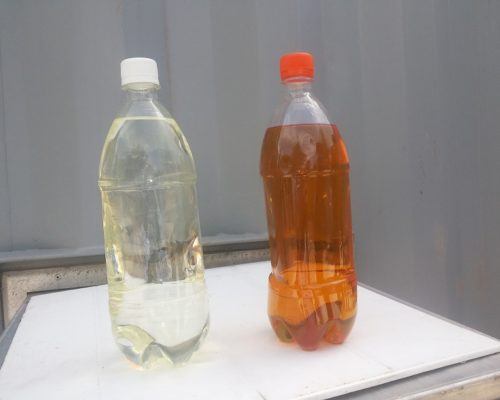
It is a well-known fact that as the transformer ages the oil inside degrades over time. The oil is exposed to unwanted elements like acids, moisture, metal dust and sometimes dissolved gases too which makes it important for us to consider filtration of transformer oil in order to maintain a good quality and clean oil for the transformer to give efficient and reliable performance.
What is the role of Transformer Oil?
Before we get into the detailed process of oil filtration it is important for us to understand the job of the transformer oil. So basically the it has two main tasks:
Advantages of Oil Filtration Process
As mentioned above, a clean and good quality is essential for efficient transformer operation. Here are few advantages of oil filtration:
- It improves the insulation properties of the oil
- The life span of transformer increases
- Decreases the transformer failure and downtime
- Increases ROI for your asset
When is Oil Filtration Required?
As the part of your preventive maintenance program, transformer oil testing should be conducted periodically. Below is a list of test which are to be done in order to determine the condition of the oil:
- Dielectric Strength or Breakdown Voltage (BDV)
- Water Content
- Neutralisation Value
- Interfacial Tension
- Colour and appearance
- Test for Oxidation Stability
- Specific Resistance (Resistivity)
- Flash Point
- Pour Point
- Viscosity
- Sludge Test
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA)
If any of the above test are outside the safe and acceptable value, then transformer oil filtration should be done immediately. For more information regarding transformer oil testing you can read our following article: Transformer Oil Testing: Types, Methods and Analysis

Oil Filtration Machine
The oil treatment process is carried out using an oil filtration machine also known as insulating oil treatment plant or IOT. These machines are generally mobile in nature and can be transported to the work site to carry out the job. Screw jacks are provided so as to release the pressure from the wheels when in stationery condition. The machine is weather proof and can be used in almost any climatic condition. The plant runs on a three phase supply of 415V, 4 wire 50Hz AC supply.
Moreover, the oil filtration machine uses specialized dosing pumps which are used to monitor volumetric flow rate of the transformer oil during the filtration process. This gives us valuable information which enables us to monitor the filtration cycles.
It comes in various capacities and is chosen depending on the rating of the transformer and the job at hand. The capacities of the oil filtration may vary from 500LPH to 16000LPH. (LPH = Litters Per Hour)

This mobile plant consists of an inlet and outlet section. The transformer oil is taken into the machine though the inlet valve using an oil pump inside the machine. The oil is then goes through the filtration system before finally being pumped out through the outlet valve back to the transformer tank or the OLTC – depends if the oil filtration process is carried out for the main tank or the OLTC. Oil hoses made of nitrile rubber are used for the oil handling operation. They are cable able to handle transformer oil up to 100°C and vacuum.
Oil Filtration Process
As mentioned above the contaminated oil from the transformer is taken through the inlet valve with the help of an inlet pump. The pump has protection against over pressure and got interlocking arrangement between pump and the heater so as to ensure that heaters in plant get energized only when the pump is switched ON. Interlocking arrangement is also provided between the pump and the high level float switch located inside the degassing chamber to avoid excessive rise of oil in the chamber.
In the first step of the filtration system, the temperature of the oil is raised to 65°C to provide latent heat which helps to separate the moisture and gases. Moreover, initial heating of the oil makes the filtration process easier as it decreases the oil viscosity.
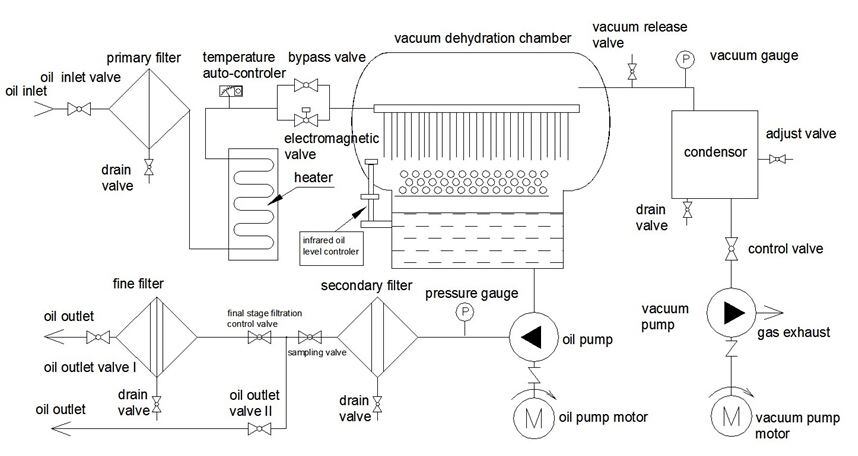
The second step is to remove the sludge and contaminants from the oil which is done generally in two ways depending on the oil filtration machine:
1. Using Filter: Modern oil filtration machines use a series of filters. Oil is first passed through Press Filter which are held between metallic discs and helps to remove impurities bigger than 50 micros. This filer helps in removing the sludge in the oil. Oil is then passed through Cartridge Filter of 1-micron rating. They have a large dust holding capacity and needs to be replaced periodically.
2. Using Centrifuging Action: As the name suggests, oil is filtered using centrifuging which helps to separate the dirt from the oil. The only advantage in this type of machines is that recurring cost of changing filters can be avoided.
Third step involves the dehydration or dehumidification of insulating oil along with degasification which helps to remove the unwanted gases and moisture. The whole process is carried out in the degassing chamber of the machine which contains two float switches – one which is electrically interlocked with the inlet pump to avoid excessive rise of oil and the second is provided to control the low level of oil which is electrically interlocked with the discharge pump. A sampling point is provided after the discharge pump for the ease of taking a sample.
Vacuum pumps are provided for the evacuation of the gas from the degassing chamber. Clean oil is then finally pumped back to the transformer using a discharge pump.
The while cycle is repeated 3-5 times till the required BDV value is achieved.

For More Information
Visit:
