All you need to know about Offshore Wind Energy Farms
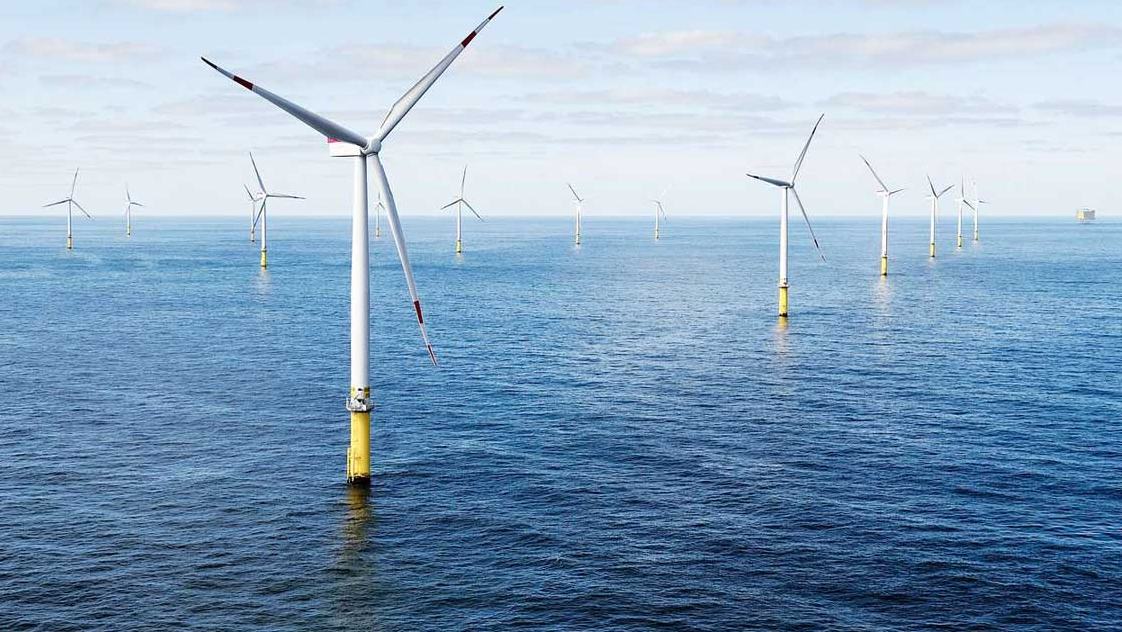
Offshore wind energy is simply a green and renewable energy which is obtained using wind energy farms deep in the oceans. This wind energy farms take advantage of the winds which is produced in high seas where the speed of the winds is quite high and relatively constant as compared to the winds on shore since there are no barriers to obstruct their path. In order to capture and make the most of the wind energy, huge wind turbines are installed in the sea equipped with the latest technical innovations. They are sometime preferred over solar energy because it proves to be more reliable source of power.
They need to be located in shallow waters with depths reaching up to 60 meters which is away from the coast, doesn’t obstruct maritime traffic or spaces of ecological interest. According to Engine which is one of the leading company in offshore power production, the potential to generate power from offshore is twice as compared to onshore wind energy farms.
How does offshore wind energy work?
Offshore wind farms take advantage of the sea winds to generate carbon free renewable energy. They work more or less in the same way as the onshore generators, the only major difference is that they are installed deep in the seas which is either anchored to the seabed or they are mounted on a floating structure.
The basic principle lies the same for both anchored and floating type wind turbines but the floating structure enables the wind turbines to be commissioned way deep in the seas where the winds are much stronger and consistent. Another benefit which it offers is the ease of installation, since there is no need to have any solid foundations made for this. Moreover, being far from the shore also means it has less impact on the visual and maritime life.
The mast of these turbines are much higher as compared to the mast of the onshore wind turbines because of which they can generate twice as much energy as their onshore counterparts since they get higher and more consistent wind speeds in the seas.
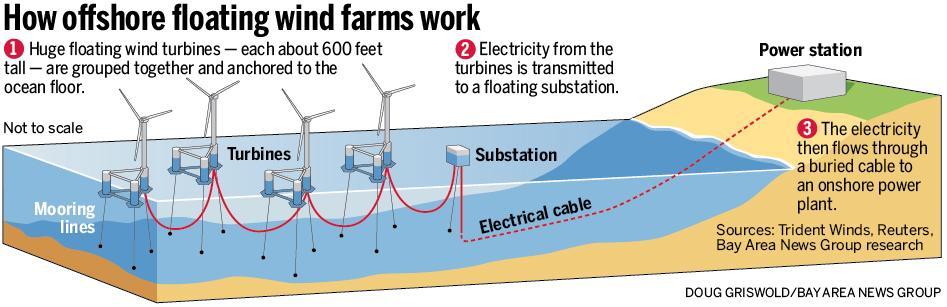
Now let’s go step by step and understand how the whole process of power generation works in offshore wind energy farms:
Largest offshore wind farm in the world !
Located in the Irish sea, the Walney Extension Offshore wind farm in the largest offshore wind farm on the planet with a generating capacity of 659 megawatts. The offshore wind farm consists of about 87 turbines which consists of 4 MHI Vestas turbines and 40 Siemens Gamesa turbines which according to one estimate is equivalent to 20,000 soccer pitches and can nearly power 600,000 homes. According to sources Orsted owns 50 percent of the project, with Danish pension funds PFA and PKA owning 25 percent each.
Offshore wind energy advantages and disadvantages
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Offshore wind speeds tend to be faster than on land, therefore better efficiency. | They are very expensive to build and maintained. |
The winds in the sea are more consistent as compared to the winds on land, therefore a more reliable source of energy. | Wave action, or very high winds especially during storms and hurricanes can damage the offshore wind energy farms. |
Since most of the urban population tends to be situated near the coastal areas, building an offshore wind farms in these areas can help us to meet those power needs. | Also the production and installation of underwater power cables to transmit the electricity can be very expensive. |
They are definitely renewable source of energy, they do not consume water, do not emit environmental pollutants or greenhouse gases etc. | Effects of offshore wind farms on marine animals and birds are not fully understood |